Convolutional Neural Network Architectures for Matching Natural Language Sentences
Published at NIPS 2015 - arXiv
Baotian Hu, et al
Hypothesis
Convolutional architechtures can help in matching natural language sentences (e.g. question and answer pairs).
Interesting methods
-
They present two architectures. In first one they basically train two convnets on the source and target sentence and they compare the final sentence embeddings with consine.
-
The disadvantage of the first model is that it does not take into account the interactions of the source and target sentences. Their second architecture addresses that by training the convnet on all possible segment concatentations of the source and destination sentences. Convolution is done on the following:
Where x and y are the source and destination sentences and k is the length of the convolution. Then 2D max pooling for window of 2x2 is performed:
\[z_{i,j}^{(2)} = \max(z_{2i-1, 2j-1}^{(1)}, z_{2i, 2j-1}^{(1)}, z_{2i-1, 2j}^{(1)}, z_{2i, 2j}^{(1)})\]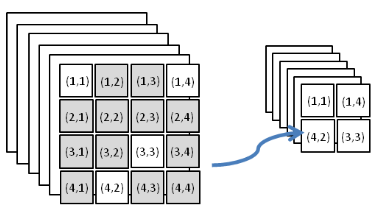
Then 2D-convolution on the output of previous layer is performed. The 2D comes from aligning segment i and j of the source and target sentences. Then max pooling and this continues.
- objective function is similar to max margin:
where they assume that the training dataset contains triples of (x,y+,y-), and s(x,y) is predicted matching score for (x,y), and \Phi includes all parameters for the convolution and fully connected layers.
Other notes
- Using padding in convolutions. Modify the convolution layer by adding a component that returns zero when the input is all zero:
where g(v) = 0 i fall the elements in vector v equals 0, otherwise g(v) = 1. This creates a natural hierarchy of all-zero padding
Experiments
All done on huge datasets.
- Matching second part of a clause with its first part (3M pairs).
- Matching responses to tweets (300K)
- MSRP Paraphrase dataset (4076 samples) – did not get state-of-the-art results in this task. Reason is the size of the dataset